Understanding the product life cycle helps organizations make better pricing decisions. With clear pricing decisions you ensure that the product survives the cut-throat market competition and stays afloat no matter how challenging the situation gets.
By adopting product life cycle pricing you ensure that the buyers are enticed to choose a brand over the others time and again. Pricing strategies can make or break a business!
The Four Product Life Cycle Pricing Strategies
1. The Market Introduction / Development Stage
At this stage, the product emerges, develops its market and spreads awareness of its qualities as well as features. In the initial stage, your business requires a significant investment of capital to manufacture products and to promote it. The risk faced by businesses at this stage is generally high: focus is on the determination of the right price point and finding their way to the minds of the consumers.
2. The Growth Stage
By this stage, consumers are familiar with your product and your brand. Your focus should be on achieving a more significant share of the market. Your product needs to stand out from the crowd. Marketing has a crucial role here: if your marketing delivers, it automatically results in increased demand forecasts and profit. Consumers are generally curious to purchase your product as they are attracted to the marketing campaign.
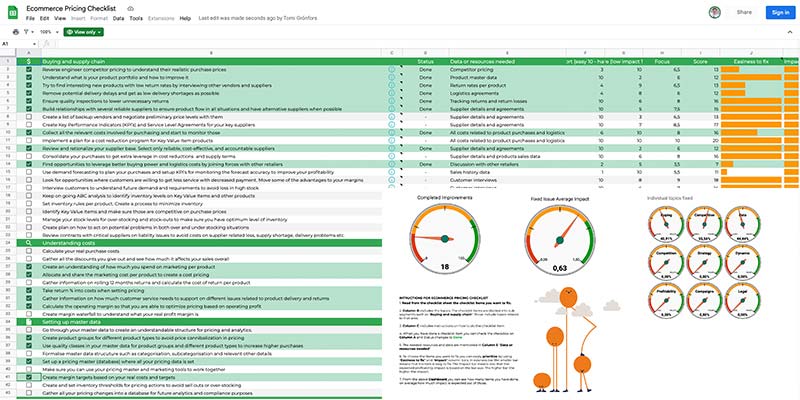
101 tips for Ecommerce Pricing
Want to improve your Ecommerce pricing? Get 101 expert tips on Ecommerce pricing and start improving your Ecommerce pricing already today.
3. Maturity Stage
Also known as the stage of saturation, businesses generally feel there is a sudden halt in revenue development as sales begin to slow down. This affects the overall growth. In general, businesses at this stage do not require funding and the brand / product stabilises in the market stage.
4. Decline Stage
This stage is often the most challenging for your product. The existence of your business faces risks as it is affected by market saturation, high competition and interest changes of consumers.
To successfully survive throughout this stage and to ensure a continuation of the products market presence, businesses start adopting aggressive marketing techniques. In other words, this is the “make it or break it” stage.
Aspects that may affect your business at this stage:
- Change in the interest of the consumer
- Your brand cannot offer anything new to the market
- Your competitors outperform in the market
Do profitable pricing with an AI-driven repricing tool
Discover how AI-powered repricing can give you a competitive edge at every stage of the product lifecycle.
Pricing in the Introduction Stage
If your product is unique and consumers are introduced to something completely new, then the prices can be fixed high. With high-prices, the massive development and promotional costs can be earned back easily.
If the launched product already faces high competition, then you must set the price lower than average to attract consumers to try out your new product.
Defining the price of a product in the initial stage is tricky. If your prices are too high, price-sensitive customers may refrain from giving your product a try, and others may consider your brand as being overly priced. On the other hand, if you set your prices too low, you might be signalling poorer quality and consumers do not trust your product.
Whether your product is unique or not, you must understand what you are offering and bringing to the market.
Pricing in the Growth Stage
Once the market has accepted you as a business, you need to focus on retaining customers. This can be done by lowering the prices. In the growth stage businesses can earn revenue to recover from the initial investments and marketing expenditure as long as they are able to set the price high enough to cover their costs.
Understand what the competitors are doing in the market and set competitive prices.
You may have to increase volumes by price matching the competitive market.
Pricing in Maturity Stage
Competition at this stage gets fierce! Brands reach a saturation point by now, and revenue production becomes very challenging. The successful way out through this is to invest in re-creating the product and revamping it entirely to create curiosity in customers.
Maturity lifecycle stage pricing examples could be: introducing special discount or promotional prices and period offer, providing privileges to the loyal members and introducing exclusive membership offer. These tactics work better than reducing the prices as they create curiosity in people.
Pricing in Decline Stage
As the market saturates and reaches its lowest, making drastic changes in the pricing helps meet the business goals. Three major evils that come into play at this point are high competition, changing customer needs and market saturation.
To tackle this stage, businesses and brands must reduce production costs and minimize production so they won’t get stuck with a huge inventory they then are forced to sell off at a minimum price. The focus must be to re-establish the name by adding new features to the product and advertise it to loyal consumers.
The lifecycle stage price elasticity varies at each development stage. With the competition rising at every stage, making a brand the top priority for the consumers becomes the most challenging part.
Through every stage that the product progresses the competition increases and makes consumers more price sensitive.
Conclusion on Life Cycle Pricing
Adopting product life cycle pricing is a tool for marketers, designers and management alike that promises overall success of a product in a market. Businesses can derive the most value out of a product/service with the help of smart pricing strategies. The rising sale will not always mean progress; neither declining sales always indicate an ultimate doom.


